damage to which of the following muscles would interfere most with the ability to breathe?
 Solved: The Axial Muscles Of The Head And Neck Are Assigne... | Chegg.com
Solved: The Axial Muscles Of The Head And Neck Are Assigne... | Chegg.comPatients and Visitors Medical Professionals For Our CommunityEmployed/Prospectives Clinics " Treatments SuppliersPrimary & Speciality CareLocations Pages, News & Articles You are here. How do spinal cord injuries affect the body? Spinal cord injuries can affect many body functions, such as: Spinal cord Reflections Normally, messages from the brain are sent through the spinal cord to parts of the body, leading to movement. When the spinal cord is damaged, the brain message cannot happen. Spinal nerves below the injury level receive signals, but they are not able to raise the spinal tracks to the brain. Reflex movements can occur, but these are not movements that can be controlled. They can occur when the foot is touched or coughed.Spinal shock This is the temporary loss of all spinal cord reflexes below the injury level. This could last days to weeks. When the spinal shock ends, spasticity or stiffness begins below the level that the spinal cord was injured. You can't prevent spinal shock and you must solve for yourself. Breathing The muscles (diaphragm, intercostal and abdominal) needed to breathe and cough can be weakened after a SCI. It takes cough to clean the lungs from secretions and bacteria. If a person has a weak cough or cannot clean the secretions of his lungs, he or she will have a higher risk of infection, such as pneumonia. A C4 or higher lesion will affect the diaphragm, the muscle that moves the lungs to breathe. A T1 to T11 lesion will affect the intercostal muscles, the muscles between the ribs. A T7 to T12 lesion will affect the abdominal muscles. The body needs diaphragm, intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles to breathe and cough well. If the SCI is cervical (in the neck), a person may need breathing support with a fan, either for a short time or forever. If a fan is needed, a breathing tube will be placed in the mouth or nose, and then attached to the fan. If the fan is needed for a long time or has many lung secretions, a person may need a tracheostomy (trach). A trach is a tube located in the trachea (wind pipe). It will make it easier to cough the flem and so the nurse will suck the lungs. At first, a person will not be able to speak while in his or her place. As you improve, you can use a talking trachón. A plot may not be permanent. If you are not in a fan, you are encouraged to cough and breathe deep per hour while awake to help keep your lungs healthy and prevent infection. You can also be asked to use an incentive spirometer, a plastic breathing device. You can see on the device how much air is taking in the lungs. The nurse or therapist will help you set goals to use this respiratory device. Families are welcome to participate in the help you use the incentive spirometer. neurogen shock (low heart rate and low blood pressure) The brain usually controls blood pressure and heart rate. Signs of the brain send messages through the spinal cord to restrict blood vessels and elevate the heart rate to maintain normal blood pressure and heart rate. When these signals can't get through, a person may have low blood pressure and slow heart rate. Blood pressure can fall when the head of the bed suddenly rises because the blood vessels below the injury level are dilated. They cannot restrict fast enough to prevent low blood pressure. This is called orthostatic hypotension. To reduce the risk of this, the head of the bed gradually rises, and you can use an abdominal folder. Changed Temperature Regulation A person may not be able to sweat or make goose blows below the injury level. The body cannot adjust its temperature. A person may feel cold and need blankets, then feel hot and needs a fan or be discovered. Autonomic hyperreflexia (also known as autonomic dysreflexia or hyperdysreflexia)People with the greatest risk for this condition are those with SCIs above T6. This tends to happen after the stage of spinal shock. Autonomic hyperreflexia occurs because nerve messages that used to raise the spinal cord to the brain are blocked. The conditions below the level of injury that can lead to autonomic hyperreflexia are: Symptoms may be:Each person may have slightly different symptoms. Autonomic hyperreflexia is a serious condition and needs to be treated immediately. The prevention and search for signs are very important. Heart attack or seizures can occur if this is not treated. This is a condition that can happen throughout the rest of your life. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)A DVT is a blood clot that can be developed in the legs and arms. It is often caused by lack of movement. Elastic media, sequential compression devices and/or foot pumps will be placed on the legs or feet to help prevent a DVT. A blood thinning medication may be used, or a filter may be placed in a blood vessel. The regular exercise of the arms and legs, and the spin will be done to help prevent the DVT from forming. Stomach HiloSometimes after a SCI, the stomach and intestine will stop working for a short time. This is called ileum. Even if the stomach isn't working, it still makes acid. Acid can damage the stomach lining and cause stomach ulcers if not eliminated. A nasogastric tube (NG) can be placed through the nose in the stomach. This tube will be used to help remove stomach acids. Medicines can also be given to help prevent stomach ulcers. Tracing Highest cervical lesions can make traction difficult. If this happens, an NG tube may be needed for nutrition and medication. The tube is placed through the nose in the stomach. The liquid formula will be given continuously or several times a day. The hospital dietitian helps the health care team choose a formula based on their calorie and liquid needs. If long-term feeding is needed, a gastric tube (G-tube tube or PEG tube) can be surgically placed through the wall of the abdomen in the stomach. Bowl Control Changes in bowel control may occur after an injury. A person may have constipation or diarrhea. An intestinal training program may be used that includes diet, medications and digital stimulation. Digital stimulation means touching within the rectum to help the intestines move. Developing an intestine training program takes time, but it can be successful. Bladder controlSCI can also cause messages between the bladder and brain to be changed. Normally, when the bladder is filled, the nerves of the bladder send a message to the spinal cord to the brain indicating the need to urinate (pee). The message to the brain can be lost after an injury. There is also no bladder tone when the spinal shock is present. At first after an SCI, a urinary catheter will be placed to drain the bladder. As the body begins to adjust to the injury, the catheter will be removed. The nurses will review the volume of the bladder. If it is full, a catheter will be put to drain the urine and then the catheter will be taken. Over time, a bladder training plan will begin. The tone of the bladder may or may not return depending on the level of your SCI. The bladder can be flaccid (weakness) or spurious (hyperactive). An urologist may be asked to evaluate the bladder and medication or surgery may be recommended. SkinSkin is a protective cover for your body. Excessive pressure, heat, or humidity may cause skin decomposition (bebidas or pressure ulcers) due to lack of blood flow and oxygen. The skin ulcer can be infected. After a SCI, the body may not be able to warn of dangers to the skin. Therefore, regular repositioning, change and complete cleaning will be required after going to the bathroom. Muscles and tendons Spasticity can occur after an SCI when the signals of the brain are blocked to the muscles. This is often not seen until the spinal shock resolves. When spasticity occurs, there is resistance to stretching muscles. It can be painful and lead to contractures, a shortening of muscles and tendons. If spasticity is a problem, it can be treated. Repositioning and medicine, such as Baclofen, can help. Botox injections can also be used. Bones and joints PainWith SCI, pain can be acute or chronic. Acute pain can be caused by bruises, broken bones, surgery or positioning. Chronic pain can be caused by excessive use of joints and muscles, or changes in muscles, joints and ligaments. Pain is treated according to the type and cause of pain. The most important thing to remember is that pain is real and there is a physical cause. Talk to the health care provider about pain. Brain injuries Many people who have had severe trauma to the neck and back can also have injuries to their brain. These may vary from mild commotion to more severe injuries. They can cause difficulty with memory, concentration or communication, and can cause personality changes. SexualityLove and intimacy are basic needs that all people share. A person with SCI still has sexual needs. There may be a loss of sensation in genitals for both men and women. The injury of each person affects their sexuality in a different way. Often, both men and women may still have sex. Men will have erections, some uncontrolled, which can be carried by sexual thoughts or as a reflection with catheterization or erotic stimulation. Maintaining an erection can be difficult. This is called erectile dysfunction (ED). There are many medical treatments to help with this. Ejacular capacity can also change. Therefore, men may have difficulties with fertility (the ability to have children). All of these functions depend on the level and degree of injury. For women, nothing prevents sexual intercourse, but vaginal secretions can be less. Women can have orgasms. For women of childbearing age, menstrual periods are often interrupted and may not start again from 3 to 6 months. Women can still become pregnant and have children, and can be delivered vaginally. Although sexual intercourse is important, love and intimacy can be shared in many ways. Touching the face and hair of a loved one, kissing, hugging, sharing ideas and problems, memories and laughing together are also important. During the acute phase of injury, your health care provider may not know how much sexual function you will have. As you progress more in your rehabilitation, it will be more likely to foresee. Talk to your health care team about any changes you may notice. Many rehabilitation centers have sexual counselling programs for patients and families, which help them understand and cope with these changes. Are you interested in using our health content? Patients and Visitors Medical Professionals For our community/prospective employees Our Website Family Iowa University Hospitals & ClinicsRight © 2021 . All rights reserved.

Solved: 64) Muscles Visible At The Body Surface Are Often ... | Chegg.com

Solved: 67) Muscles Located Entirely Within An Organ Are C... | Chegg.com

Solved: The Muscle(s) That Insert(s) On The Tibial Tuberos... | Chegg.com

Damage to which of the following muscles would interfere most with the ability | Course Hero

ch. 10 Flashcards | Quizlet

Damage to which of the following muscles would interfere most with the ability | Course Hero

ch. 10 Flashcards | Quizlet

Damage to which of the following muscles would interfere most with the ability | Course Hero

ch. 10 Flashcards | Quizlet

Damage to which of the following muscles would interfere most with the ability | Course Hero

ch. 10 Flashcards | Quizlet

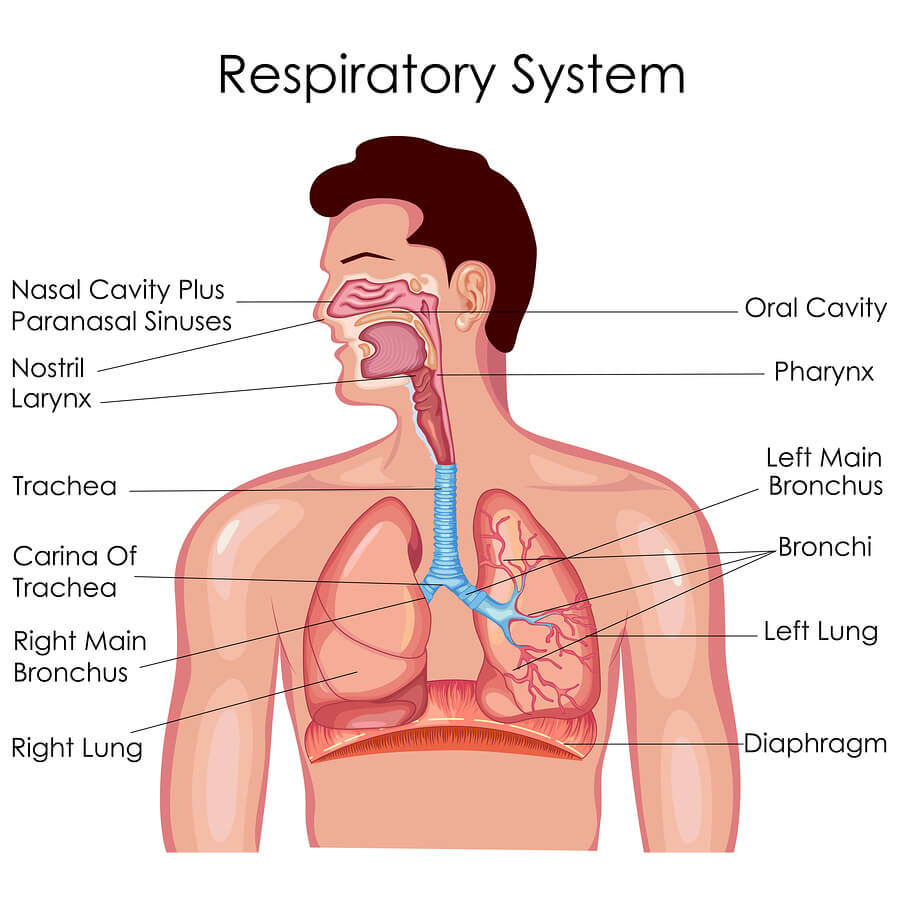
The Process of Breathing | Anatomy and Physiology II

Damage to which of the following muscles would interfere most with the ability | Course Hero

The Effects of Stroke on the Body

10 Most Common Symptoms of Gastritis | gastritis symptoms back pain,fatigue and dizziness

ch. 10 Flashcards | Quizlet

COVID-19 and Respiratory System Disorders | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Weakness - Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerve Disorders - Merck Manuals Consumer Version
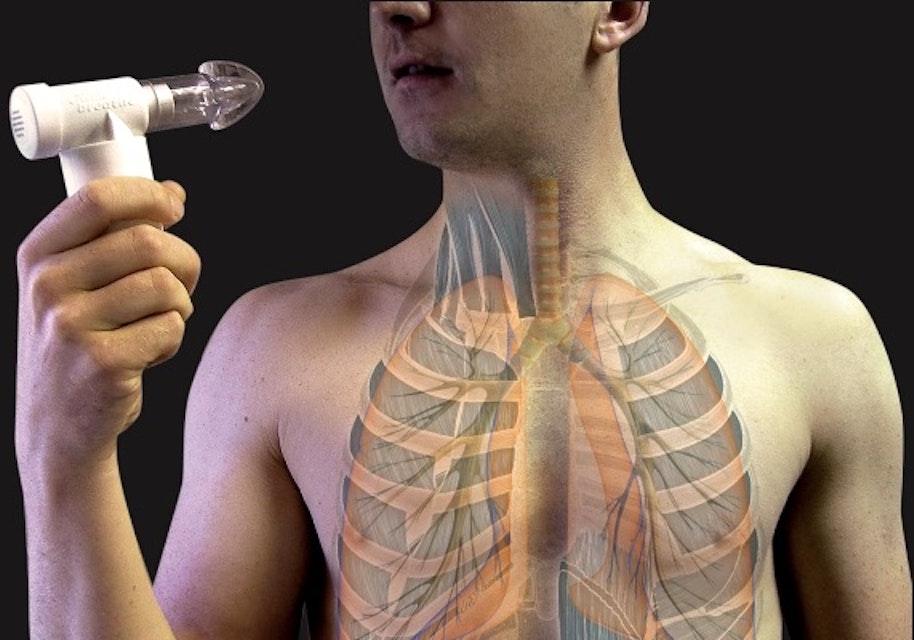
Diaphragmatic Breathing Exercises - Physiopedia
What Drugs Can Cause Breathing Problems - Substance Abuse on the Respiratory System
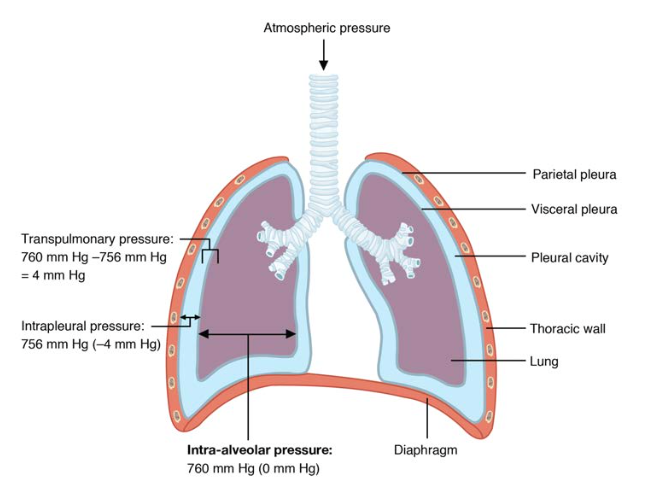
The Process of Breathing | Anatomy and Physiology II

Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and National Kidney Foundation: Revised 2020 Standards of Practice and Standards of Professional Performance for Registered Dietitian Nutritionists (Competent, Proficient, and Expert) in Nephrology Nutrition - Journal
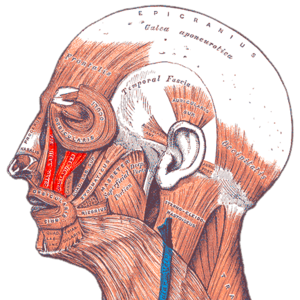
Facial Muscles - Lower Group - Physiopedia
Life with a C-Spine Injury: How to Avoid Respiratory Complications

What is a contusion (bruise)? Bones, muscles, and more
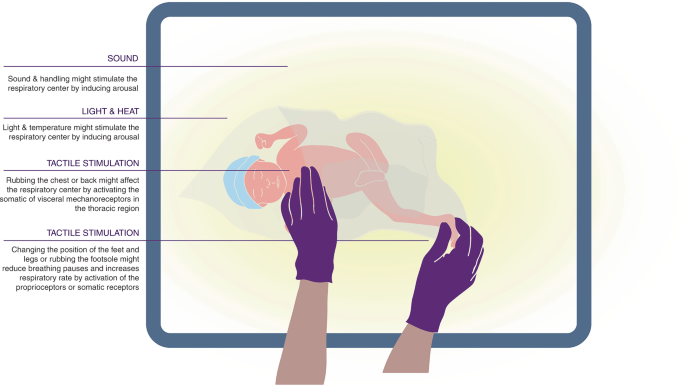
Stimulating and maintaining spontaneous breathing during transition of preterm infants | Pediatric Research

Smoke Inhalation: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prognosis

Emphysema - Lung Health A-Z - CHEST Foundation

Looking at Masks and Respiratory Health - The New York Times
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/breathing--x-ray-680800663-599c577f03f40200118056ce.jpg)
Diaphragm: Anatomy, Function, and Abnormalities
Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease

Spinal Cord Injury - ScienceDirect
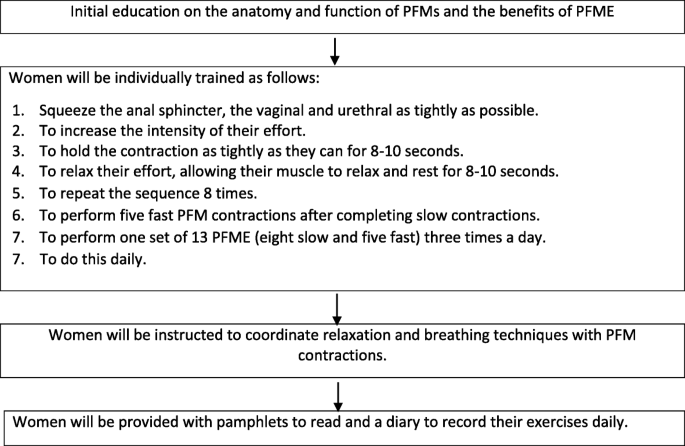
Evaluation of the effect of an antenatal pelvic floor muscle exercise programme on female sexual function during pregnancy and the first 3 months following birth: study protocol for a pragmatic randomised controlled

Why cancer may leave you short of breath and tips for breathing easier | CTCA
Correct Breathing and "Support" for Singing — SingWise

Hyperthyroidism Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatments - Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, and support

CHAPTER 10 Question and Answers Flashcards | Quizlet
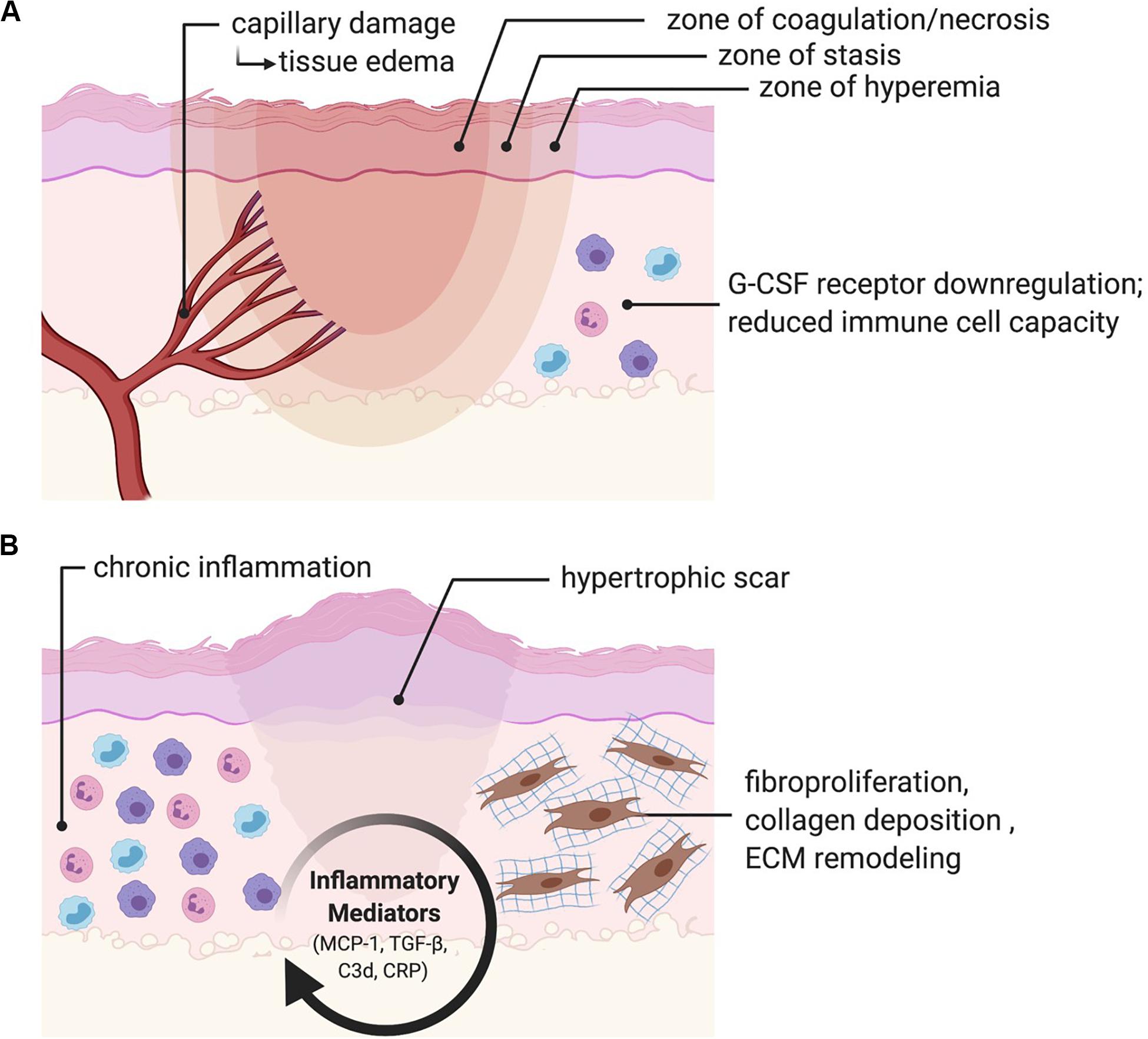
Frontiers | Current and Emerging Topical Scar Mitigation Therapies for Craniofacial Burn Wound Healing | Physiology
Interferences between breathing, experimental dyspnoea and bodily self-consciousness | Scientific Reports
Posting Komentar untuk "damage to which of the following muscles would interfere most with the ability to breathe?"